Virtual Serial COM Port
Virtual COM port (หรือ Virtual Serial Port) คือ การจำลองพอร์ต COM ของคอมพิวเตอร์เพื่อให้สามารถเชื่อมต่อกับอุปกรณ์ภายนอกที่ใช้สื่อสารแบบซีเรียลได้ โดยใช้ซอฟต์แวร์ที่ช่วยทำหน้าที่จำลองพอร์ต COM ขึ้นมา เพื่อสร้างสายสัญญาณควบคุมการสื่อสารระหว่างคอมพิวเตอร์กับอุปกรณ์ภายนอก
ตัวอย่างของซอฟต์แวร์ที่ใช้ Virtual COM port เช่น Serial-to-Ethernet Converter ซึ่งเป็นเครื่องมือที่ช่วยแปลงสัญญาณซีเรียลเป็นสัญญาณเครือข่ายแบบ Ethernet ซึ่งสามารถเชื่อมต่อกับคอมพิวเตอร์ผ่านทาง Virtual COM port ได้
Virtual Serial Port Emulators
HW VSP3 – Virtual Serial Port
HW VSP is a software driver that adds a virtual serial port (e.g. COM5) to the operating system and redirects the data from this port via a TCP/IP network to another hardware interface, which is specified by its IP address and port number.
Licence type: Freeware
pass : admin
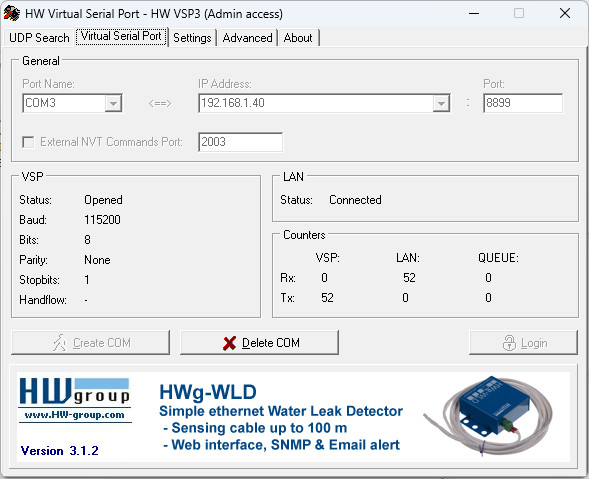
Serial Test reslut Method 1 Arduino
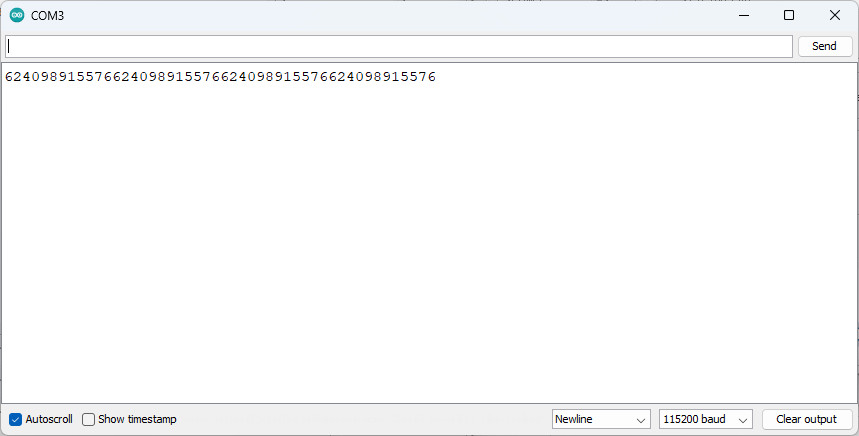
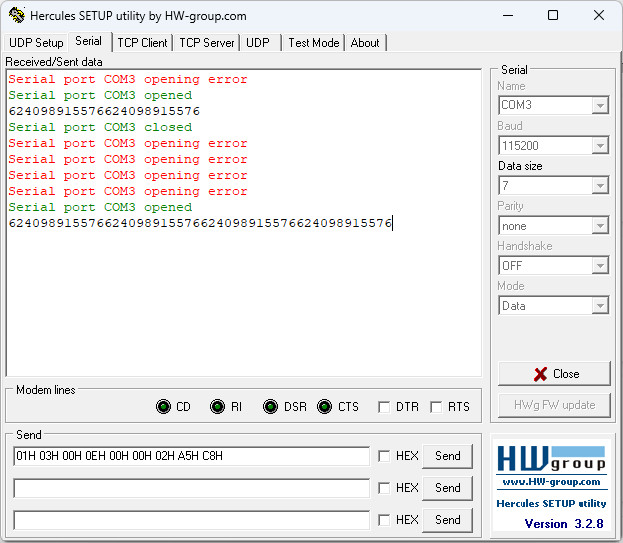
Serial Test reslut Method 2 Hercules
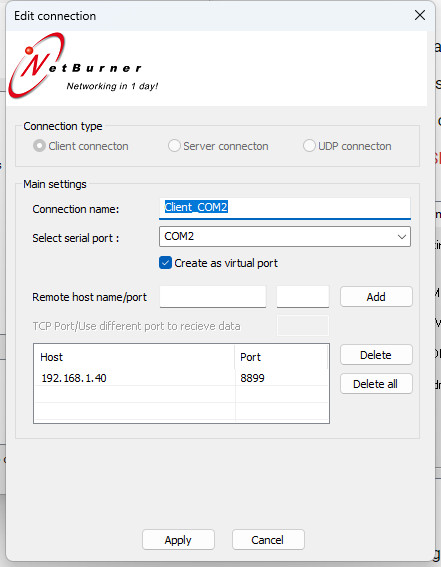
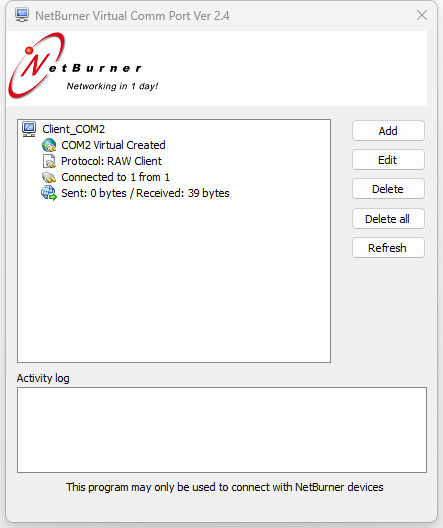
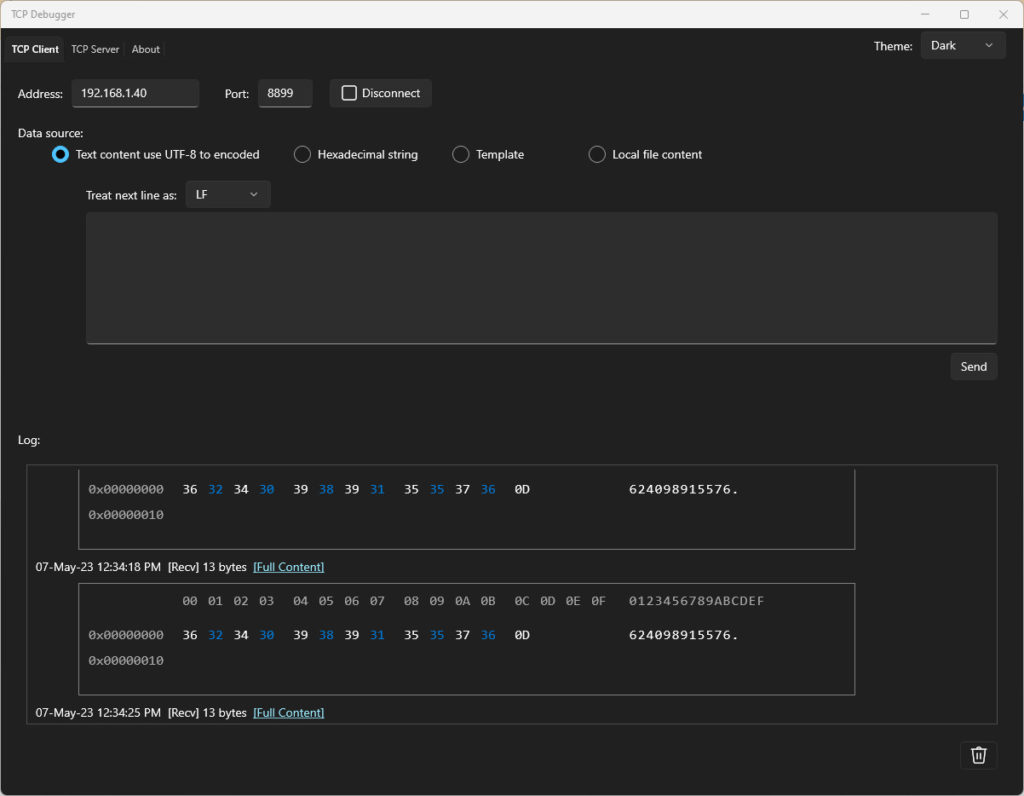
Virtual COM Port Driver software (https://www.netburner.com/)
https://www.netburner.com/learn/how-to-create-a-virtual-serial-port/